
Β-Thalassemia Intermedia (β +/β Silent or β 0/β Silent or β Silent/β Silent): 2 Patients are asymptomatic and have mild anemia that can worsen under conditions of stress. Patient is able to sufficiently produce enough β globin chains to maintain normal oxygenation and red blood cell lifespan. One β globin chain gene is mutated while the other β globin chain gene is normal. Β globin chain genes mutation does not result in any abnormal hematological findings and β globin chain production is normal or nearly normal. Β-Thalassemia Silent Carrier (β Silent/β): 2 These point mutations cause production of β globin chains to be reduced (β +) or abolished completely (β 0). β-thalassemia is usually due to point mutations in the β globin genes. Β globin chain genes are located on chromosome 11 and there are normally two genes in total (β/β) one inherited from each parent. Hb Barts: 10-40% at birth, traces in adults Heinz Bodies and Hb H inclusions (Supravital Stain).Poikilocytosis: targets, tears, ellipto, schisto, sphero, etc.The marked tissue hypoxia usually results in fetal death in utero or shortly after birth.
Due to its high affinity for oxygen, it is not able to efficiently transport oxygen to the tissues of the developing fetus. Excess γ globin chains result in the formation of Hb Barts. Occurs when all four α genes are deleted (no α globin chain production).īecause no sustainable amount of α globin chains is produced, this state is usually considered to be incompatible with life. Hydrops Fetalis/ α-Thalassemia Major (–/–): 1 Production of Hb Barts at birth is increased. Hb H is unstable and often precipitates within red blood cells resulting in hemolytic anemia. The excess β globin chains form tetramers known as Hemoglobin H (Hb H). Patients present with a chronic hemolytic anemia that varies from mild to moderate. α gene production is significantly reduced (75% reduction) causing a higher imbalance between the number of α and β globin chains being produced.

From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, Hemoglobin H inclusions are seen in the red blood cells (Golf-ball like). From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, Ī supravital stained Hemoglobin H Disease peripheral blood smear. In adults, globin chain production is balances, so no Hemoglobin H is formed.Īn image of a Hemoglobin H Disease peripheral blood smear showing marked poikilocytosis (tearsdrop cells, schistocytes, target cells, and elliptocytes). There is between 5-15% hemoglobin Barts present at birth, but this decreases once β globin chain production takes over and γ globin chain production decreases. Patients are asymptomatic and any anemia present is mild. In adults, increased production of red blood cells is able to compensate for the decrease in α chain production, and α and β globin chain production is balanced. There is now a 50% reduction in normal α globin chain production. In the silent carrier state, there is only a small amount of Hb Barts produced. Hb Barts has a high oxygen affinity and is inefficient for oxygen delivery to the tissues of the developing fetus. These γ globin chains tend to also form tetramers and result in Hemoglobin Barts (Hb Barts). In newborns, there is an excess production of γ globin chains.

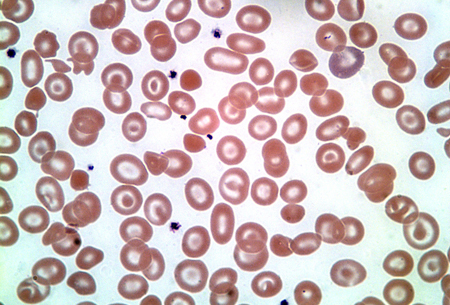
Patient is asymptomatic and the mutation is benign. There is still adequate production of α to ensure normal hemoglobin synthesis. Α-Thalassemia Silent Carrier (αα/α-): 1,2 The severity of anemia and amount of α globin chain production is dependent the number of genes that are deleted. α-thalassemia results when there is a deletion in any number of the α globin gene. Α globin chain genes are located on chromosome 16 and there are normally four genes in total (αα/αα), two inherited from each parent. This is considered to be a quantitative hemoglobin disorder and is categorized by the affected globin chain (alpha or beta), and as major or minor depending on the severity of the disease. Thalassemias are classified as a group of genetic hemoglobin disorders where the production of α and β globin chains is affected. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta. Images show thalassemia peripheral blood smears with hypochromic, microcytic red blood cells and poikilocytosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
